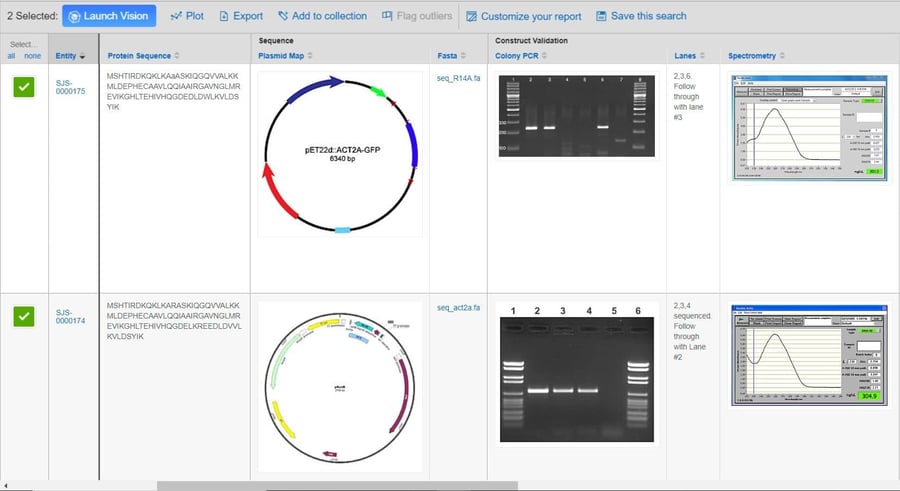
Biologics play a key role in today’s modern drug discovery research. It’s no surprise that recent enhancements to the CDD Vault platform have been geared toward the registration and analysis of biological entities.
Vault Configuration to Support Biological Entities
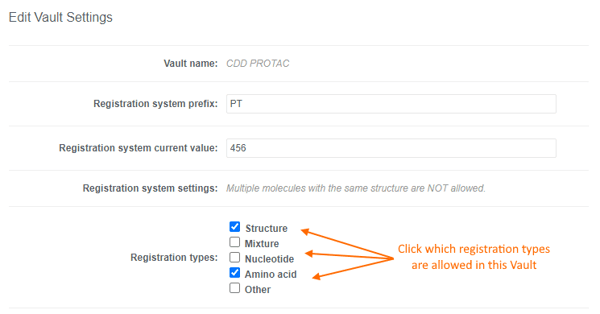
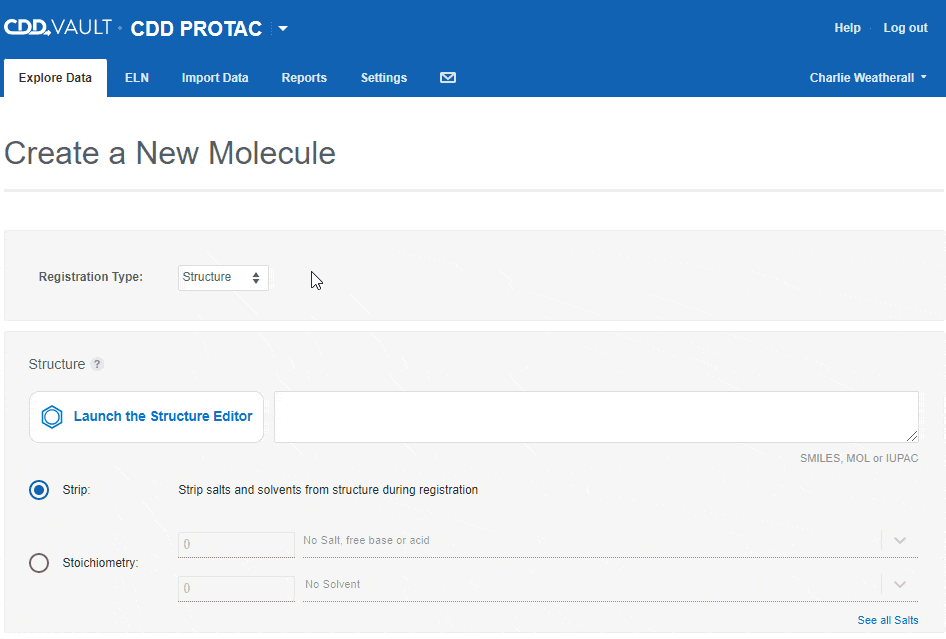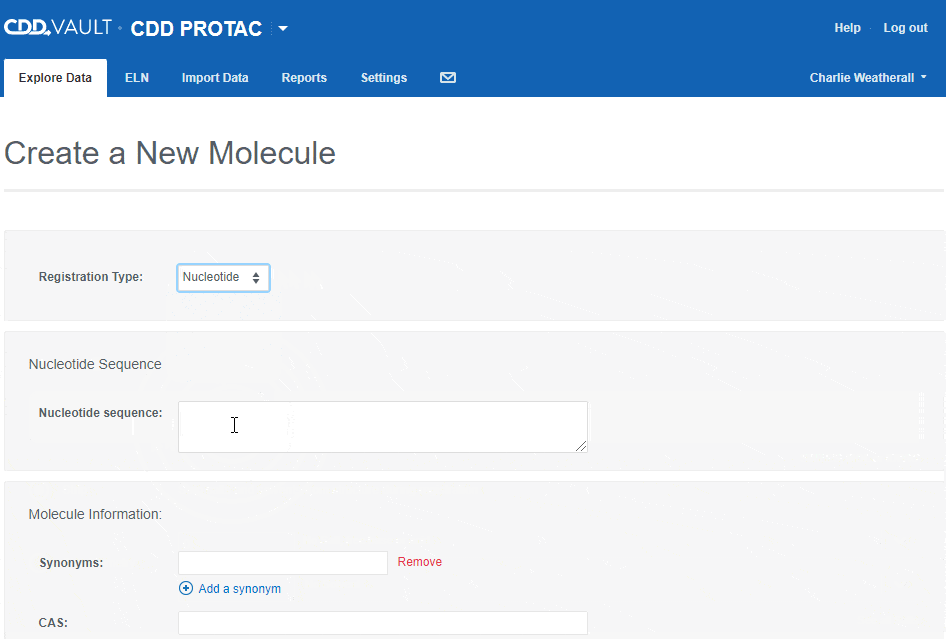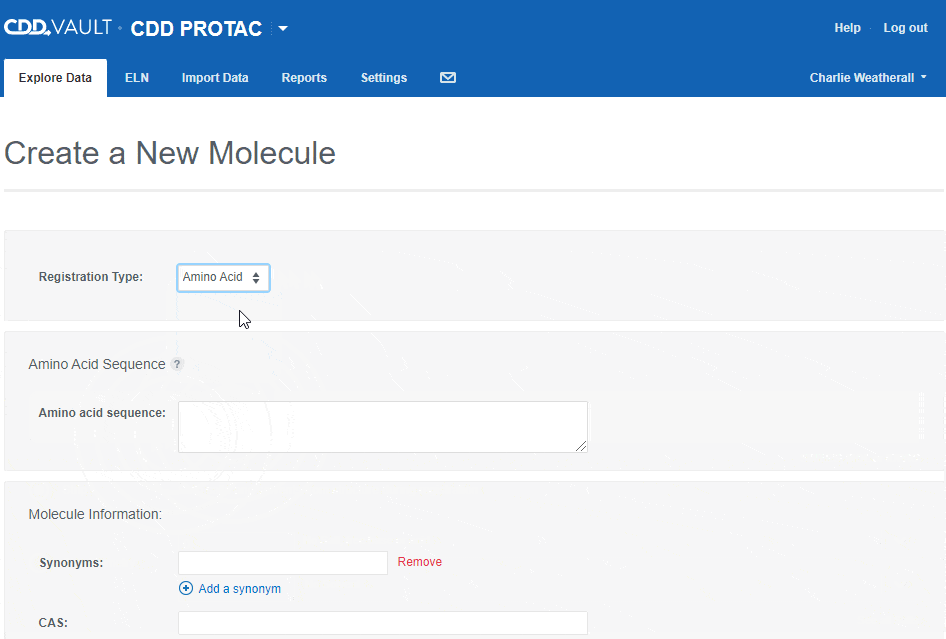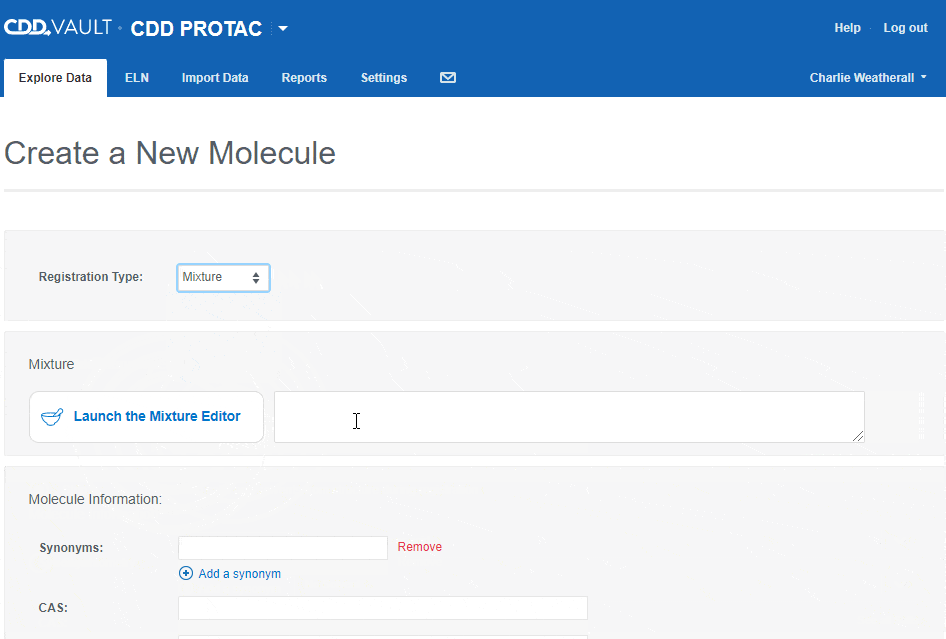
Users can accurately capture different entities in CDD Vault using the following "Registration types":- Structure
- Nucleotide
- Amino acid
- Mixture
- Other
 Noteworthy tip:
Noteworthy tip:
- A single Vault can be configured to allow the registration of multiple registration types.
- You may decide to only allow 1 registration type in a given Vault, and request additional Vaults for other registration/entity types. This allows you to configure the Entity Fields to the specific registration type in each Vault.
- Registration types can be toggled on and off without impacting registered entities.
- “Other” is ideal for cell lines, blood/tissue samples, consumables, etc. and can be combined with a must be unique field so any unique criteria can be used. Or simply leverage the registration ID & batch name in your downstream workflows.
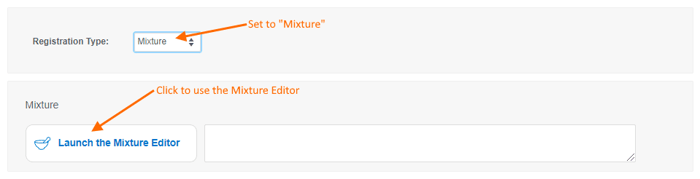
- Mixtures will be discussed in detail in a future release note. For now, let us know what you think of the mixtures editor and feel free to contact Support with questions.
Registering Biological Entities
If the Vault Administrator allows registration of more than one entity in a Vault, the "Create a New Molecule" workflow will include an initial drop-down to select the type.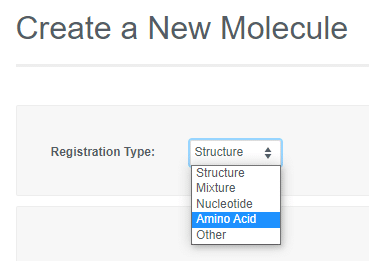 Depending on the registration type selected, you can then paste in a sequence or launch an appropriate editor to register the desired entity.
Depending on the registration type selected, you can then paste in a sequence or launch an appropriate editor to register the desired entity.
To register a new Nucleotide sequence:
- choose the "Nucleotide" registration type,
- type or paste a nucleotide sequence into the text box (or leave it blank to create a sequence-less record),
- enter values for the available data fields, and
- click the "Create" button.
- the input may be lower or upper case, and
- only the A, C, G, T, U, and N (wildcard) codes are allowed.
- Spaces and line breaks are ignored.
 Once registered, the nucleotide sequence is displayed along with the Composition and Sequence Properties that are automatically generated by CDD Vault.
Once registered, the nucleotide sequence is displayed along with the Composition and Sequence Properties that are automatically generated by CDD Vault.
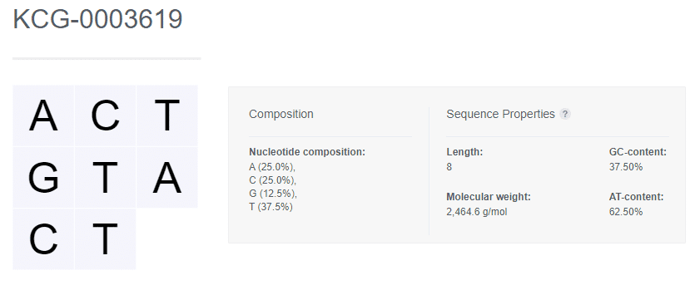 Nucleotide Sequence Properties
Length The number of nucleotide bases in the sequence
Molecular weight The sum of the molecular weights of the nucleotides and an end weight correction. The compounds are treated as single-stranded sequences with hydroxyl ends (no phosphate on either end). The compound is assumed to be DNA unless uracil is present. Molecular weight cannot be calculated for sequences containing ambiguous codes (i.e. N) For DNA, the equation follows [number of A] * 313.210 + [number of T] * 304.195 + [number of C] * 289.184 + [number of G] * 329.209 - 61.964 For RNA, the equation follows [number of A] * 329.209 + [number of U] * 306.167 + [number of C] * 305.183 + [number of G] * 345.208 - 61.964
GC-content The percentage of explicit guanine and cytosine in the sequence
ATU-content The percentage of explicit adenine and thymine/uracil in the sequence
Nucleotide Sequence Properties
Length The number of nucleotide bases in the sequence
Molecular weight The sum of the molecular weights of the nucleotides and an end weight correction. The compounds are treated as single-stranded sequences with hydroxyl ends (no phosphate on either end). The compound is assumed to be DNA unless uracil is present. Molecular weight cannot be calculated for sequences containing ambiguous codes (i.e. N) For DNA, the equation follows [number of A] * 313.210 + [number of T] * 304.195 + [number of C] * 289.184 + [number of G] * 329.209 - 61.964 For RNA, the equation follows [number of A] * 329.209 + [number of U] * 306.167 + [number of C] * 305.183 + [number of G] * 345.208 - 61.964
GC-content The percentage of explicit guanine and cytosine in the sequence
ATU-content The percentage of explicit adenine and thymine/uracil in the sequence
To register an Amino Acid sequence:
- choose the "Amino Acid" registration type,
- type or paste an amino acid sequence into the text box (or leave it blank to create a sequence-less record),
- Enter values for the available data fields, and
- click the "Create" button.
- Registration supports sequences of 1-letter or 3-letter amino acid codes.
- All non-alphabetical characters, including spaces, are ignored.
- To register a sequence of 1-letter codes:
- Sequence must be entirely uppercase.
- Example: LRVILCA
- To register a sequence of 3-letter codes:
- Amino acid codes must follow the capitalization format upper-lower-lower.
- Any delimiters are ignored.
- Example 1: LeuArgValIleLeuCysAla
- Example 2: Leu-Arg-Val-Ile-Leu-Cys-Ala
 Once registered, the sequence of the Nucleotide entity is displayed along with the Composition and Sequence Properties that are automatically generated by CDD Vault.
Once registered, the sequence of the Nucleotide entity is displayed along with the Composition and Sequence Properties that are automatically generated by CDD Vault.
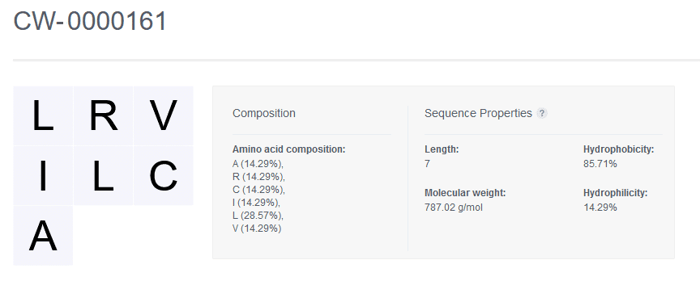 Amino Acid Sequence Properties
Length The number of amino acids in the sequence
Molecular weight The sum of the molecular weights of the amino acids plus the weights of the ends. The molecules are treated as sequences with a hydroxyl end and a hydrogen end. Molecular weight cannot be calculated for sequences containing ambiguous codes (i.e. B, Z, X)
Hydrophobicity The percentage of explicit hydrophobic amino acids (A, C, F, I, J, L, M, V, W) in the sequence
Hydrophilicity The percentage of explicit hydrophilic amino acids (B, D, E, K, N, Q, R, Z) listed in the sequence
Amino Acid Sequence Properties
Length The number of amino acids in the sequence
Molecular weight The sum of the molecular weights of the amino acids plus the weights of the ends. The molecules are treated as sequences with a hydroxyl end and a hydrogen end. Molecular weight cannot be calculated for sequences containing ambiguous codes (i.e. B, Z, X)
Hydrophobicity The percentage of explicit hydrophobic amino acids (A, C, F, I, J, L, M, V, W) in the sequence
Hydrophilicity The percentage of explicit hydrophilic amino acids (B, D, E, K, N, Q, R, Z) listed in the sequenceOther posts you might be interested in
View All Posts
Webinars
1 min
October 23, 2025
Augmented Design: Practical Applications of LLMs and Agentic Workflows in Medicinal Chemistry
Read More
Webinars
1 min
October 23, 2025
Distributed Operations: Building Competitive Advantage in Biotech Through Strategic Outsourcing
Read More
Webinars
1 min
October 23, 2025
OpenADMET Blind Challenge
Read More